Nitrogen is a non-metallic elements in the periodic table is in group VA or class 15 has the symbol N and atomic number 7. At room temperature in the form of gas is colorless, odorless, tasteless and form diatomic elements (N2). Nitrogen has also disbursed colorless and odorless
Figure formula Molecular nitrogen and liquid nitrogen
Nitrogen is very difficult to react with other elements or compounds that are called by the name of nitrogen. Nitrogen is the most gas in the atmosphere is about 78%. In addition to the atmosphere, nitrogen is also present in the planet mars (3%).
Chemical bond between two atoms in a nitrogen molecule is the strongest bond between two atoms of the same element. This makes gas N2 is very stable and inert. In a living creature's body tissue, mostly containing nitrogen, such as proteins and nucleic acids to be one of the fundamental building blocks of DNA and RNA.
There are two stable isotopes of nitrogen are: 14N and 15N. Isotope 14N is at most (99 634%), resulting in the stars and the rest are 15N.
In the industry of nitrogen derived from the melting air with a high enough pressure, followed by fractional distillation or fractional distillation.
When nitrogen is heated, can react directly with magnesium, lithium and calcium.
6 Li + N2 → 2 Li3N
3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
When mixed with oxygen and subjected to electric sparks, forming nitric oxide (NO) and then became dioxide (NO2). When heated under pressure with hydrogen and the presence of a suitable catalyst will form ammonia (Haber process).
Nitrogen compounds are widely used in industry and in the laboratory of nitric acid and ammonia (the most in the industry). Ammonia, NH3 is a toxic nitrogen hydride is the most important raw material for chemical nitrogen and chemicals is one of the most widely produced in the world. Ammonia is used as a base material such as urea nitrogen fertilizer and explosives.
Preparation NITROGEN IN THE LABORATORY
In the laboratory, nitrogen was prepared by heating a mixture of ammonium chloride and sodium nitrite and a little water. If ammonium nitrite is heated it decomposes produce nitrogen gas. However, this reaction is very fast and may be explosive.
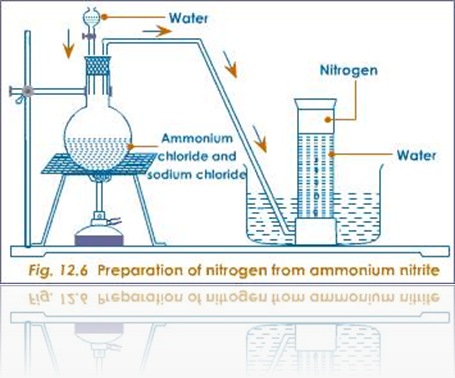
For security, campukan ammonium chloride and sodium nitrite with a mass ratio of 4:5, and then heated with a little water. The presence of water prevents mensublimasi ammonium chloride when heated. Initially, the two substances undergo double decomposition to form sodium chloride and ammonium nitrite.
Ammonium nitrite is formed and then breaks down into nitrogen gas and water.
Nitrogen gas formed kemudia flowed through the water like in the picture. In this way the moisture will be left behind while the nitrogen gas hold up because of the low solubility in water.
ACID NITRATE
Nitric acid is a strong acid which is corrosive and toxic and breaks down into H + and NO3-ions in the water equation
Ordinary nitric acid has a concentration of 68%. HNO3 solution with a concentration of over 86% is referred to as fuming nitric acid. Pure nitric acid is a colorless liquid that can be turned into a yellowish red because of the dissolved nitrogen oxides and red at high temperatures. HNO3 a white solid color at temperatures below -41 ° C and boils at 83 ° C.
Nitric acid is a strong oxidizer so handling should be careful. When the members of the body be washed under running water.
Pictures of pure nitric acid yellowish due to dissolved nitrogen oxides and 70% nitric acid is colorless
water King
A mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid with a ratio of 3:1 (ie 3 mL HCl with 1 mL of HNO3 or HCl to 1 L 3L HNO3) is called water king because it can dissolve precious metals like gold and platinum. Aqua regia is very unstable, so newly created aqua regia when it will be used.
The properties of nitric acid
Nitric acid is a strong oxidizer that readily releases oxygen so the storage should be placed separately and avoid organic ingredients are generally flammable. In a chemical reaction when high concentrations, HNO3 reduced to NO2, while at low concentrations reduced to NO.
Warming HNO3 will unravel produce NO2.
The reaction of nitric acid with a non-metallic and metallic
Being a strong oxidizing agent, nitric acid reacts violently with many non-metals, metal compounds, and the reaction may take place explosive. Except for gold and platinum, HNO3 reacts with virtually all metals.
The product is dependent on the nature of the metal (metal reactivity), acid concentration and temperature. Reaction with the less reactive metal gaseous NO reduction results when used while concentrated HNO3 NO2 gas reduction results. Some examples of the reaction of nitric acid as follows.
The reaction of carbon with nitric acid
C + 4HNO3 → CO2 + 4NO2 + 2H2O
3C + 4HNO3 → 3 CO2 + 4NO + 2H2O
The reaction of sulfur and iodine with nitric acid
S(s) + 2HNO3(aq) → H2SO4(aq) + 2NO(g) (HNO3 intense cold)
3I2(s) + 10HNO3(aq) → HIO3(aq) + 2H2O(l) + 10NO(g) (HNO3 intense hot)
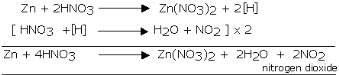
The reaction of zinc with nitric acid
The reaction of magnesium with nitric acid
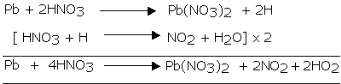
The reaction of lead with nitric acid
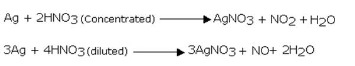
The reaction of silver with nitric acid
Trinitro Toluena (TNT)
A mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid when reacted with toluene is obtained a compound called trinitro Toluene (TNT). Trinitro toluene is a compound that is very ekplosif.


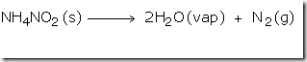






0 komentar
Post a Comment